17. Pricing Strategy
Pricing Strategy Heading
Pricing Strategy
ND036 C4 L02 A12 Pricing Strategy
Pricing Strategy Example

Pricing Strategy Recap
Factors to Consider When Setting Pricing
- What value does the user get from using the product?
- What does the product cost to produce?
- What is your company's goal for the product?
- What do competitors charge?
Things to Remember About Pricing
- The price can't be higher than the value your users get from the product
- In most cases, the price can't be lower than the long term cost to produce it
- The product's price must be consistent with goals for the product
- The price can't be higher than a competitor's price, unless you have a product that does a better job of meeting the user's need
Pricing Models
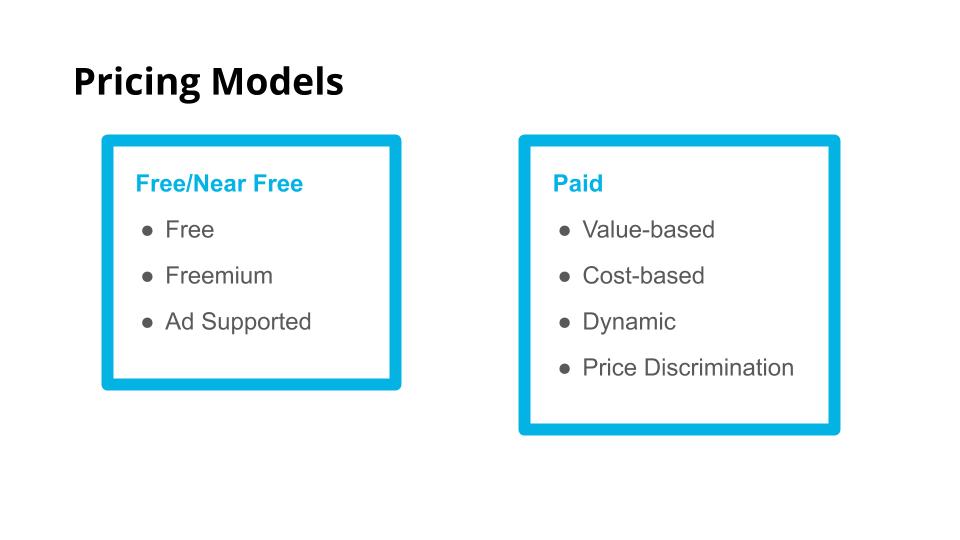
Pricing models recap
New Terms
Ad Supported: The product is free, but it generates revenue from advertisers.
Cost-based pricing: The cost to produce the product is the base price and a mark-up is added.
Dynamic pricing : Price changes reflect changes in supply or demand, e.g. surge pricing.
Freemium: The basic product is free but you can purchase additional features or content, e.g. Dropbox.
Price discrimination: Different users are charged a different price for the same product, e.g. US airline tickets.
Value-based pricing: Price is based on the value the user gets from the product.
As a PM, it is not your job to be a pricing expert. But you do need to understand the basic principles of pricing strategy and how your product fits in.
Pricing Strategy Exercise
SOLUTION:
TruePricing Model Definitions
QUIZ QUESTION::
Match each definition to its pricing model
ANSWER CHOICES:
|
Definition |
Pricing Model |
|---|---|
The product doesn’t cost anything |
|
Price varies based on the user you are selling the product to |
|
Price fluctuates based on marketplace dynamics, like supply and demand |
|
Price is based on how the user perceives the benefits of the product |
|
Price is based on the effort it takes to produce the product, plus a markup |
|
Revenue is generated by displaying sponsored content in the product |
|
Parts of the core product don’t cost anything but you can purchase additional functionality |
SOLUTION:
|
Definition |
Pricing Model |
|---|---|
|
Price is based on how the user perceives the benefits of the product |
|
|
Price fluctuates based on marketplace dynamics, like supply and demand |
|
|
Revenue is generated by displaying sponsored content in the product |
|
|
Price is based on the effort it takes to produce the product, plus a markup |
|
|
The product doesn’t cost anything |
|
|
Parts of the core product don’t cost anything but you can purchase additional functionality |
|
|
Price varies based on the user you are selling the product to |
Pricing Strategy Exercise
SOLUTION:
- Generating revenue
- Market dominance
- Reducing costs
Airline Ticket Pricing Strategy
QUIZ QUESTION::
Airline ticket prices vary widely and use multiple pricing models. In each of the situations below, a passenger will pay a higher than average ticket price. Which pricing model is the primary driver of a higher price?
ANSWER CHOICES:
|
Ticket Purchase Scenario |
Pricing Influence |
|---|---|
Holiday weekend ticket |
|
Student discount |
|
Long distance route |
|
Business Class ticket |
SOLUTION:
|
Ticket Purchase Scenario |
Pricing Influence |
|---|---|
|
Student discount |
|
|
Holiday weekend ticket |
|
|
Business Class ticket |
|
|
Long distance route |